Products

There are multiple types and grades of thermocouple wire. Each type of thermocouple wire has a specific combination of metal alloys. This combination is what defines the type of thermocouple. For example, a type K thermocouple is made when a wire of Nickel-Chromium is welded to a wire of Nickel-Alumel. The grade of the wire is dependent not only on the combination of alloys used, but also on the purity of those alloys. For a full list of thermocouple types and corresponding thermocouple wires, see our thermocouples types page
Thermocouple grade wire is used to manufacture thermocouple probes. Thermocouple grade wire is normally used for the junction and inside the stem sheath. This is because the thermocouple grade wire has a accuracy specification than extension grade wire.
Extension grade wire is a less expensive, lower grade wire. It is used to extend from the thermocouple probe to the control system or digital display. Extension grade wire is more economical due to the length requirements. Also, it is not in the process itself and does not play as critical a role nor does it experience the temperature extremes & temperature cycling.
In many industrial applications a sensor is located in a process pipe far away from the control room. This means a wire must be run a considerable distance back to the control room to get the temperature reading. Using more expensive thermocouple grade wire to accomplish this is unnecessary. Extension grade wire will do the job.
Standard limits of Error: These thermocouples use standard “thermocouple grade” wire and make up the great majority of sensors.
Special Limits of Error: These thermocouples are made with a higher grade of thermocouple wire that is purer than standard wire, which increases their accuracy. They are more expensive than standard thermocouples.
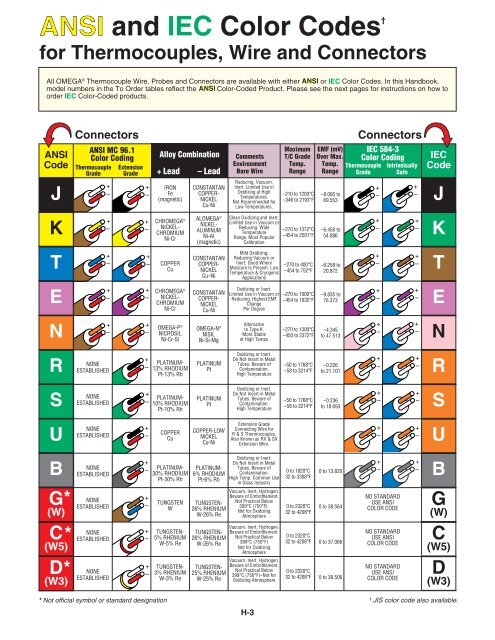
A thermocouple can be identified by the color of its wire insulation. For example, in the United States a type J thermocouple has one red wire and one white wire, typically with a brown over jacket. A type J extension grade wire also has one red wire and one white wire, but it has a black over jacket. As a general rule the red wire of a thermocouple or extension wire is negative and the positive wire is color coded according to the type of thermocouple. Different countries use different color codes.
Visit our Thermocouple Color Codes page for a complete list.
 Type J Thermocouple
Type J Thermocouple
Type J (iron–constantan) has a more restricted range (−40 °C to +750 °C)
 Type K Thermocouple (Nickel-Chromium / Nickel-Alumel)
Type K Thermocouple (Nickel-Chromium / Nickel-Alumel)
Type K (chromel–alumel) is the most common general-purpose thermocouple with a sensitivity of approximately 41 μV/°C.[11] It is inexpensive, and a wide variety of probes are available in its −200 °C to +1350 °C (−330 °F to +2460 °F) range
 Type T Thermocouple (Copper/Constantan)
Type T Thermocouple (Copper/Constantan)
Type T (copper–constantan) thermocouples are suited for measurements in the −200 to 350 °C range.
 Type N Thermocouple (Nicrosil / Nisil)
Type N Thermocouple (Nicrosil / Nisil)
Type N (Nicrosil–Nisil) thermocouples are suitable for use between −270 °C and +1300 °C, owing to its stability and oxidation resistance. Sensitivity is about 39 μV/°C at 900 °C, slightly lower compared to type K.
 Type E Thermocouple (Nickel-Chromium/Constantan)
Type E Thermocouple (Nickel-Chromium/Constantan)
Type E (chromel–constantan) has a high output (68 μV/°C), which makes it well suited to cryogenic use. Additionally, it is non-magnetic. Wide range is −270 °C to +740 °C and narrow range is −110 °C to +140 °C.
 Type B Thermocouple (Platinum Rhodium – 30% / Platinum Rhodium – 6%)
Type B Thermocouple (Platinum Rhodium – 30% / Platinum Rhodium – 6%)
Type B (70%Pt/30%Rh–94%Pt/6%Rh, by weight) thermocouples are suited for use at up to 1800 °C.
 Type R Thermocouple (Platinum Rhodium -13% / Platinum)
Type R Thermocouple (Platinum Rhodium -13% / Platinum)
Type R (87%Pt/13%Rh–Pt, by weight) thermocouples are used 0 to 1600 °C.
 Type S Thermocouple (Platinum Rhodium - 10% / Platinum)
Type S Thermocouple (Platinum Rhodium - 10% / Platinum)
Type S (90%Pt/10%Rh–Pt) thermocouples, similar to type R, are used up to 1600 °C.
 Type G Thermocouple
Type G Thermocouple
(W–74%W/26%Re)
 Type C Thermocouple
Type C Thermocouple
Type C Thermocouples are made from Tungsten Rhenium alloys and designed for extreme high temperatures up to 4,200°F (2315°C). (95%W/5%Re–74%W/26%Re).
 Type D Thermocouple
Type D Thermocouple
(97%W/3%Re–75%W/25%Re)
Type D thermocouple has Tungsten with 3% Rheniumfor the positive leg and Tungsten with 25% Rhenium
for the negative part.
 Type M Thermocouple
Type M Thermocouple
Type M (82%Ni/18%Mo–99.2%Ni/0.8%Co, by weight) are used in vacuum furnaces for the same reasons as with type C (described below). Upper temperature is limited to 1400 °C. It is less commonly used than other types.
Request A Quote

Call For a Quote:
+91 9326071660Email Address:
[email protected]